 |
| Postmenopausal Uterus (Postmenopausal Bleeding) |
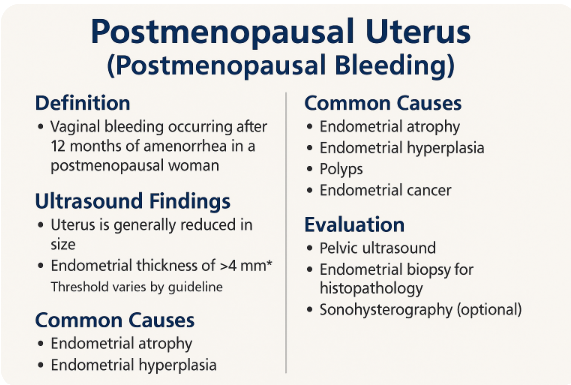
1. Introduction to Postmenopausal Uterus 100%
Definition: Cessation of menses ≥12 months
Common Clinical Concern: Postmenopausal Bleeding (PMB)
Role of Ultrasound: First-line modality
Screening for endometrial and adnexal pathology
Common Clinical Concern: Postmenopausal Bleeding (PMB)
Role of Ultrasound: First-line modality
Screening for endometrial and adnexal pathology
2. Normal Postmenopausal Uterus Appearance 100%
Uterus: Small, atrophic, homogeneous
Endometrial Thickness: ≤4 mm in asymptomatic women
Cervix: May appear prominent compared to the uterus
No endometrial fluid or mass expected
Endometrial Thickness: ≤4 mm in asymptomatic women
Cervix: May appear prominent compared to the uterus
No endometrial fluid or mass expected
3. Scanning Technique 100%
Transvaginal Ultrasound (TVS) – gold standard
Transabdominal Scan – used if TVS not feasible
Measurement of endometrial stripe in sagittal plane
Color Doppler to assess vascularity in lesions
Transabdominal Scan – used if TVS not feasible
Measurement of endometrial stripe in sagittal plane
Color Doppler to assess vascularity in lesions
4. Evaluation of Postmenopausal Bleeding 100%
Assess endometrial thickness (cutoff: 4–5 mm)
Identify focal lesions: polyps, fibroids, masses
Look for fluid collections, irregular endometrium
Evaluate ovaries for masses or cysts
Use saline infusion sonography (SIS) if needed
Identify focal lesions: polyps, fibroids, masses
Look for fluid collections, irregular endometrium
Evaluate ovaries for masses or cysts
Use saline infusion sonography (SIS) if needed
5. Common Pathologies Detected 100%
1. Benign Conditions
Endometrial PolypSubmucosal Fibroid
Endometrial Hyperplasia (simple/complex)
Endometrial Atrophy (commonest cause of PMB)
2. Malignant or Suspicious
Endometrial Carcinoma (irregular, thickened stripe, >5 mm)Cervical Cancer (distorted cervix, mass effect)
Ovarian Malignancy (complex masses)
Uterine Sarcoma (rare, aggressive masses)
6. Role of Doppler and SIS 80%
Doppler: Increased vascularity in malignancy
SIS: Enhances evaluation of polyps and fibroids
Useful in indeterminate or thickened endometrium
Helps plan hysteroscopic biopsy if needed
SIS: Enhances evaluation of polyps and fibroids
Useful in indeterminate or thickened endometrium
Helps plan hysteroscopic biopsy if needed
7. Management Guidance Based on US Findings 90%
Endometrial thickness ≤4 mm: Conservative follow-up
Thickness >5 mm or irregular: Further evaluation/biopsy
Focal lesions: Hysteroscopy or curettage
Persistent PMB: Always investigate thoroughly
Thickness >5 mm or irregular: Further evaluation/biopsy
Focal lesions: Hysteroscopy or curettage
Persistent PMB: Always investigate thoroughly
8. Case Studies and Quiz Section 0%
Endometrial Polyp vs Carcinoma case
Ultrasound diagnosis of Atrophic Endometrium
Doppler pattern analysis in PMB
Quiz on normal vs abnormal postmenopausal uterus
Ultrasound diagnosis of Atrophic Endometrium
Doppler pattern analysis in PMB
Quiz on normal vs abnormal postmenopausal uterus








No comments:
Post a Comment