Fetal l cerebroplacental ratio (CPR)
The fetal brain receives moderate blood flow (higher MCA PI) to match developmental needs.
Resistance in the umbilical artery increases (UA PI ↑).
The fetus compensates by vasodilating cerebral arteries (MCA
PI ↓) — a phenomenon called the “brain-sparing effect”.
So, low CPR = compromised fetal condition.
Doppler Technique: How is CPR Measured?
🌀 1. Umbilical
Artery (UA) PI
Sample Location: Preferably in a free-floating loop of the cord (mid-portion, not near the fetus or placenta).
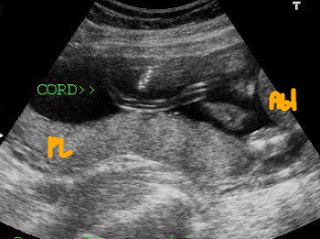 |
| Free loop of umbilical cord (not near fetal abdomen or placenta) |
Angle: As close to zero as possible (Ideally, <60°, but exact angle correction is not required for PI).
Waveform: Should show clear systolic and diastolic flow.
 |
| show clear systolic and diastolic flow. |
Doppler: Umbilical artery doppler value by weeks in third trimester.
| Gestational Age (Weeks) | PSV (cm/s) | EDV (cm/s) | RI | PI | S/D Ratio | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | ~55–60 | ~18–22 | ~0.65–0.70 | ~1.1–1.2 | <4.0 | Beginning of 3rd trimester |
| 29 | ~58–62 | ~20–24 | ~0.64–0.68 | ~1.05–1.2 | <3.8 | Gradual decline in RI, PI |
| 30 | ~60–63 | ~22–26 | ~0.63–0.67 | ~1.0–1.1 | <3.5–3.8 | Increasing diastolic flow |
| 31 | ~61–64 | ~24–27 | ~0.62–0.66 | ~1.0 | <3.5 | |
| 32 | ~62–66 | ~25–28 | ~0.61–0.65 | ~0.95–1.05 | <3.2–3.5 | Better placental perfusion |
| 33 | ~63–67 | ~26–30 | ~0.60–0.64 | ~0.95–1.0 | <3.2 | |
| 34 | ~64–68 | ~27–31 | ~0.60–0.63 | ~0.9–1.0 | <3.0–3.2 | Threshold S/D ratio <3 |
| 35 | ~65–69 | ~28–32 | ~0.58–0.62 | ~0.9–0.95 | <3.0 | Doppler values stabilize |
| 36 | ~66–70 | ~29–33 | ~0.57–0.61 | ~0.9 | <2.8–3.0 | |
| 37 | ~67–71 | ~30–34 | ~0.56–0.60 | ~0.85–0.9 | <2.8 | Near-term, resistance drops |
| 38 | ~68–72 | ~31–35 | ~0.55–0.59 | ~0.85 | <2.6–2.8 | |
| 39 | ~69–73 | ~32–36 | ~0.55–0.58 | ~0.8–0.85 | <2.5–2.7 | Normal placental aging |
| 40 | ~70–74 | ~33–37 | ~0.55–0.58 | ~0.8 | <2.5 | Full term |
Record: Pulsatility Index
(PI) — automated on most machines.
🧠 2. Middle
Cerebral Artery (MCA) PI
Sample Location: Proximal third of the MCA near its origin from the circle of Willis.
Plane: Axial (transventricular or transthalamic plane).
Angle: ≤15 degrees is ideal.
Waveform: Should be clean, with diastolic flow.
Record: Pulsatility Index
(PI).
Doppler: MCA doppler value by weeks in third trimester.
| Gestational Age (Weeks) | PSV (cm/s) | EDV (cm/s) | RI | PI | S/D Ratio | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | ~55–60 | ~18–22 | ~0.65–0.70 | ~1.1–1.2 | <4.0 | Beginning of 3rd trimester |
| 29 | ~58–62 | ~20–24 | ~0.64–0.68 | ~1.05–1.2 | <3.8 | Gradual decline in RI, PI |
| 30 | ~60–63 | ~22–26 | ~0.63–0.67 | ~1.0–1.1 | <3.5–3.8 | Increasing diastolic flow |
| 31 | ~61–64 | ~24–27 | ~0.62–0.66 | ~1.0 | <3.5 | |
| 32 | ~62–66 | ~25–28 | ~0.61–0.65 | ~0.95–1.05 | <3.2–3.5 | Better placental perfusion |
| 33 | ~63–67 | ~26–30 | ~0.60–0.64 | ~0.95–1.0 | <3.2 | |
| 34 | ~64–68 | ~27–31 | ~0.60–0.63 | ~0.9–1.0 | <3.0–3.2 | Threshold S/D ratio <3 |
| 35 | ~65–69 | ~28–32 | ~0.58–0.62 | ~0.9–0.95 | <3.0 | Doppler values stabilize |
| 36 | ~66–70 | ~29–33 | ~0.57–0.61 | ~0.9 | <2.8–3.0 | |
| 37 | ~67–71 | ~30–34 | ~0.56–0.60 | ~0.85–0.9 | <2.8 | Near-term, resistance drops |
| 38 | ~68–72 | ~31–35 | ~0.55–0.59 | ~0.85 | <2.6–2.8 | |
| 39 | ~69–73 | ~32–36 | ~0.55–0.58 | ~0.8–0.85 | <2.5–2.7 | Normal placental aging |
| 40 | ~70–74 | ~33–37 | ~0.55–0.58 | ~0.8 | <2.5 | Full term |
Percentile Growth Chart of Cerebroplacental Ratio
| Gestational Age | 5th Percentile | 10th Percentile | 50th Percentile | 90th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 weeks | 1.35 | 1.45 | 1.75 | 2.10 |
| 28 weeks | 1.20 | 1.30 | 1.60 | 1.95 |
| 32 weeks | 1.10 | 1.20 | 1.50 | 1.85 |
| 36 weeks | 1.00 | 1.10 | 1.40 | 1.75 |
| 40 weeks (Term) | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.30 | 1.60 |
Clinical Significance-Low CPR (<5th percentile)
Normal CPR
- Adequate placental function.
- Low risk of fetal distress.
Abnormal (Low) CPR
- Suggests fetal adaptation to hypoxia
or placental insufficiency.
- Associated with:
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
- Preeclampsia
- Preterm birth
- Cesarean delivery for fetal distress
- Low Apgar scores
- NICU admission
- CPR <1.0 or <5th percentile →
higher risk of adverse outcomes.
Clinical Significance- High CPR (>90th percentile)
Interpretation:
- A CPR above the 90th percentile means that the fetus
has relatively low resistance in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) and/or higher
resistance in the umbilical artery (UA).
- This is not typically considered a clinical concern.
- It often reflects normal or even favorable fetal
circulatory adaptation, especially in low-risk pregnancies.
- Not associated with adverse outcomes in the
majority of cases.
- No additional intervention is generally
required unless other risk factors or Doppler anomalies are present.
- It may occasionally be seen in early gestation
or in fetuses with high MCA vasodilation, but without compromise.
But Be
Cautious If...
If CPR >90th
percentile is seen alongside other abnormal findings (e.g., abnormal biometry,
abnormal AFI, maternal conditions), then:
- Full evaluation should be done, including
biophysical profile and possibly fetal echo.
- Rarely, a very high CPR may be seen in some
congenital heart conditions due to altered hemodynamics — but this is rare
and would usually be accompanied by other anomalies.
When to Use CPR?
- Routine in high-risk pregnancies,
especially:
- IUGR
- Hypertension/pre-eclampsia
- Diabetes
- Decreased fetal movement
- Oligohydramnios
- Post-term pregnancies
It’s not yet universally
recommended for low-risk pregnancies but is gaining traction.
🧠 CPR < 5th Percentile vs > 90th Percentile
| Feature | CPR < 5th Percentile | CPR > 90th Percentile |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Interpretation | Abnormal – potential sign of fetal compromise | Normal – often reassuring |
| Cause | ↑ UA resistance and/or ↓ MCA resistance (brain-sparing) | ↓ UA resistance and/or ↑ MCA resistance |
| Associated with | Fetal Growth Restriction (FGR), hypoxia, preeclampsia | Typically normal growth, low-risk pregnancies |
| Fetal Adaptation | Brain-sparing effect (vasodilation of MCA) | Possibly increased cerebrovascular resistance |
| Monitoring Required? | ✅ Yes – increased surveillance, possible early delivery | ❌ No (unless other risk factors present) |
| Common in | High-risk pregnancies, placental insufficiency | Healthy fetuses, or early gestation |
| Outcome Risk | ↑ Risk of adverse perinatal outcome | Generally low risk |
| Management Strategy | Doppler follow-up, biophysical profile, CTG, delivery planning | Routine care |
Quick Summary
| CPR | < 5th percentile | > 90th percentile |
|---|---|---|
| ⚠️ Risk Level | High-risk indicator | Low-risk / Reassuring |
| 🩺 Clinical Action | Increased fetal monitoring | Typically no intervention |
| 📉 What it means | Possible placental insufficiency | Good perfusion and balance |
How to Read a CPR Percentile Chart
CPR Calculator
Fetal CPR Percentile Calculator
Fetal CPR Case study
CPR=UCA PI/MCA PI
CPR=0.72/0.97
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Preeclampsia
Preterm birth
Cesarean delivery for fetal distress
Low Apgar scores
A CPR of 0.74 at 35 weeks, falling below the 5th percentile with a 10/8 PBB score, indicates abnormal fetal circulation suggestive of adaptation to hypoxia or placental insufficiency. This finding is associated with an increased risk of adverse perinatal outcomes, including IUGR, preeclampsia, preterm birth, cesarean delivery for fetal distress, and low Apgar scores. Close monitoring and timely intervention are essential to optimize neonatal outcomes.
If your BPP score was 10/8, it likely means that out of a total score of 10, 8 points came from the ultrasound (excluding the NST), which is still considered within a reassuring range. However, if the CPR is low, it can still indicate an underlying risk — especially if other signs, such as fetal growth restriction (IUGR), are also present.
Biophysical Profile (BPP) – Overview
The Biophysical Profile (BPP) is a prenatal ultrasound evaluation used to assess fetal well-being, especially in high-risk pregnancies. It combines ultrasound and non-stress test (NST) findings to evaluate the baby’s condition.
BPP Components (Each scored 0 or 2):
1. Fetal Breathing Movements – At least 1-episode lasting 30+ seconds.2. Gross Body Movements – At least 3 discrete movements.
3. Fetal Tone – At least 1 episode of active extension and return to flexion.
4. Amniotic Fluid Volume (AFV) – One pocket ≥2 cm in vertical diameter.
5. Non-Stress Test (NST) – Reactive fetal heart rate with accelerations.
Scoring:
Each component is scored 2 points (normal) or 0 points (abnormal).
Maximum score: 10
Score Interpretation:8–10: Reassuring/Normal
6: Equivocal—may require follow-up or further testing.
4 or below: Abnormal—suggests possible fetal compromise, may warrant delivery or further evaluation.

















No comments:
Post a Comment