Axial Resolution Explanation
Axial Resolution refers to the ability of an ultrasound system to distinguish two objects or structures that are located along the path of the sound beam, i.e., in the same line of sight, but at different depths. Essentially, it's the ability to differentiate two objects that are positioned parallel to the ultrasound beam.
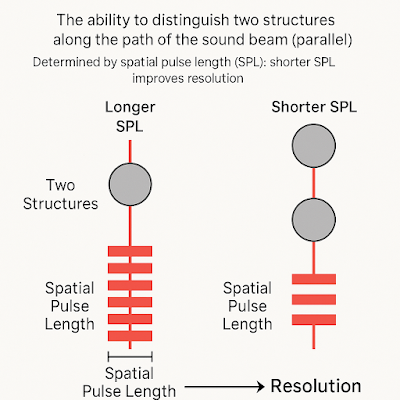
In ultrasound imaging, axial resolution is determined by the Spatial Pulse Length (SPL), which is the distance that a single pulse of sound travels through the body. SPL depends on the frequency of the ultrasound wave and the duration of the pulse. The shorter the SPL, the better the axial resolution.
Key Concepts:
-
Spatial Pulse Length (SPL): The distance the sound pulse travels during its duration. A shorter pulse length results in better axial resolution.
-
Higher Frequency = Shorter SPL: High-frequency ultrasound waves produce shorter pulses, which enhance the ability to resolve small, closely spaced structures along the sound beam’s path.
-
Lower Frequency = Longer SPL: Low-frequency waves have longer pulses and, therefore, lower axial resolution.
Improving Axial Resolution
-
Shorter Pulses: Ultrasound systems with shorter spatial pulse lengths improve axial resolution by reducing the distance between structures that can be distinguished.
-
Higher Frequency Transducers: Higher frequencies result in shorter wavelengths, which improve the axial resolution.
Diagram Idea
Here’s a conceptual breakdown of how axial resolution works:
-
Two Structures: Imagine two structures (cysts or organs) positioned at different depths along the path of the ultrasound beam.
-
Longer SPL: If the SPL is long, the system might struggle to differentiate between the two structures because their echoes overlap.
-
Shorter SPL: A shorter SPL allows the system to clearly distinguish between the structures, as their echoes will be separated enough for the system to distinguish the two.
Let me generate a diagram that visually explains this concept with examples of long and short SPL in relation to axial resolution.










No comments:
Post a Comment