1. Introduction 100%
Role of Ultrasound in Small Bowel Evaluation
Clinical Indications: Pain, Diarrhea, Obstruction, Bleeding
Comparison with CT/MRI and Endoscopy
Advantages and Limitations
Clinical Indications: Pain, Diarrhea, Obstruction, Bleeding
Comparison with CT/MRI and Endoscopy
Advantages and Limitations
2. Anatomy and Physiology 100%
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum Overview
Layered Wall Structure: 5-Layer Pattern
Wall Thickness Norms
Peristalsis and Fluid-Gas Content
Mesentery and Vascular Landmarks
Layered Wall Structure: 5-Layer Pattern
Wall Thickness Norms
Peristalsis and Fluid-Gas Content
Mesentery and Vascular Landmarks
3. Scanning Techniques 100%
Curvilinear and High-Frequency Linear Probe
Graded Compression Technique
Supine and Left Lateral Decubitus Views
Color Doppler for Vascularity
Segmental Survey (RLQ to LUQ)
Graded Compression Technique
Supine and Left Lateral Decubitus Views
Color Doppler for Vascularity
Segmental Survey (RLQ to LUQ)
4. Normal Small Bowel Appearance 100%
Wall Thickness < 3 mm (Non-distended)
Preserved Mucosal Folds (Valvulae Conniventes)
Regular Peristalsis
Compressibility and Luminal Content
No Free Fluid or Gas Abnormalities
Preserved Mucosal Folds (Valvulae Conniventes)
Regular Peristalsis
Compressibility and Luminal Content
No Free Fluid or Gas Abnormalities
5. Bowel Diseases 100%
Enteritis (Infective / Inflammatory)
Crohn’s Disease
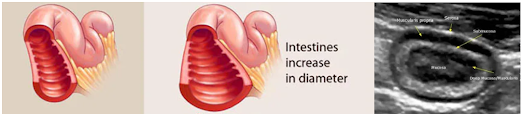
Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)
Intussusception
Mesenteric Adenitis
Small Bowel Neoplasm
Lymphoma
Carcinoid Tumor
Celiac Disease
Ischemic Bowel Disease
Tuberculous Enteritis
Typhoid Enteritis
Radiation Enteritis
Meckel’s Diverticulum
Foreign Body Impaction
Strangulated Hernia involving Small Bowel
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Bezoars
Small Intestinal Fistulas
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
Ascariasis intestinal
Crohn’s Disease
Small Bowel Obstruction (SBO)
Intussusception
Mesenteric Adenitis
Small Bowel Neoplasm
Lymphoma
Carcinoid Tumor
Celiac Disease
Ischemic Bowel Disease
Tuberculous Enteritis
Typhoid Enteritis
Radiation Enteritis
Meckel’s Diverticulum
Foreign Body Impaction
Strangulated Hernia involving Small Bowel
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Bezoars
Small Intestinal Fistulas
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
Ascariasis intestinal
6. Interventional and Follow-Up Role 0%
Ultrasound-Guided Fluid Aspiration (Abscesses)
Monitoring of Treatment in Crohn’s Disease
Follow-Up of Submucosal Lesions
Postoperative Evaluation (Leaks, Obstruction)
Monitoring of Treatment in Crohn’s Disease
Follow-Up of Submucosal Lesions
Postoperative Evaluation (Leaks, Obstruction)
7. Case Studies and Quiz Section 0%
Acute Appendicitis vs Crohn’s Ileitis
SBO with Transition Point Localization
CEUS in Small Bowel Mass Evaluation
Interactive MCQs with Annotated Images
SBO with Transition Point Localization
CEUS in Small Bowel Mass Evaluation
Interactive MCQs with Annotated Images










No comments:
Post a Comment